Abstract
Background: The development of drugs targeting BTK and BCL2 have dramatically improved the therapeutic landscape in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). However, resistance to these agents have been reported due to non-recurrent changes in oncogenic pathways and gene expression signatures. The bromodomain and extra terminal (BET) family proteins (BRD2, BRD3, BRD4 and BRDT) are epigenetic reader proteins that recognize acetylated lysine residues in histones. They play a critical role in mediating gene transcription and have been considered as highly promising targets in several diseases including cancer. Of these, the BRD4 protein is highly enriched in super enhancers and regulate gene transcription of relevant oncogenes such as MYC, CDK genes, cyclin-D1, BCL2 and MCL-1. BRD4 inhibitors (BRD4i) block the transcription of these key oncogenes through the displacement of BRDs and other epigenetic modifiers from chromatin. In this study, we investigated the preclinical activity of BRD4i PLX51107, and their cooperative role with BCL2 inhibitor Venetoclax in CLL.
Methods: 56 primary CLL cells were isolated via histopaque-1077 (Sigma-Aldrich, St Louis MO) from peripheral blood apheresis samples from consenting adults using Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center protocol CIC-01-16. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) were seeded at 3 x106/mL in a 384 or 6 well tissue culture plates and exposed to different doses of PLX51107 (1-20uM) as a single agent or in combination with Venetoclax (1-100nM) for 48 and 72hrs (Selleck Chemicals, Houston TX). Cell viability was assessed using Cell Titer-glo (Promega, Madison WI) with all data being normalized to untreated controls. Synergy was calculated using Calcusyn (Cambridge, UK) software to determine Coefficient of Synergy (CI) values. Anti-tumor effect was also analyzed by induction of apoptosis using Annexin-V/PI staining by flow cytometry at 72hrs. Cells pellets were saved for western blotting to determine expression of BRD4 members and different members of the B-cell receptor, NF-kB pathway as also the BCL-2 family of proteins. Bcl-2 family profiling was performed via Milliplex Bcl-2 family protein panels 1 and 2 to look at overall changes in Bcl-2 family expression.
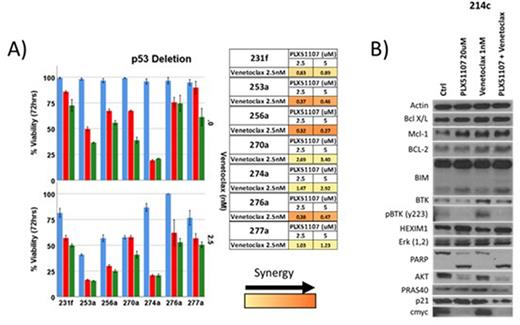
Results: Single agent exposure to PLX51107 displayed time and dose dependent induction of apoptosis of CLL cells (Figure 1a). Next, we examined the interaction between the PLX51107 and Venetoclax. In 72hr exposure the combination of PLX51107 with Venetoclax with an ATM deletion was synergistic in 4 of 8 samples and 4 of 7 samples with p53 deletion. Annexin/PI staining yielded apoptotic cell death in the single agent and combination exposure with Venetoclax. Western blotting showed a modulation of both BRD4 proteins as well as Bcl-2 family member proteins (Figure 1b). Bcl-2 family profiling via Milliplex panels demonstrated the ratio of Bcl-2/Bcl x/L was much higher in samples with a high Venetoclax IC50 (136/1) compared to Venetoclax low IC50 (54/1).
(Figure 1) -A) Samples with p53 deletion and corresponding synergy. (B) BCL2 family protein expression of CLL sample 214c.
Conclusions: Our data indicates that a) PLX51107 has an antitumor effect in CLL cells; b) the combinational treatment of Venetoclax with PLX51107 highly improved the apoptotic effect of single agent treatments. A better understanding of the key signaling pathways for CLL cells' proliferation and survival impacted by BRD4i in combination with Venetoclax would provide a proof-of-concept rationale for studies validating BRD4i as epigenetic approach to target BCR signaling in CLL.
Disclosures
Torka:Genentech: Consultancy; TG Therapeutics: Consultancy; ADC Therapeutics: Consultancy; Lilly USA: Consultancy; Epizyme: Consultancy; Targeted Oncology, Physician Education Review: Honoraria.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal